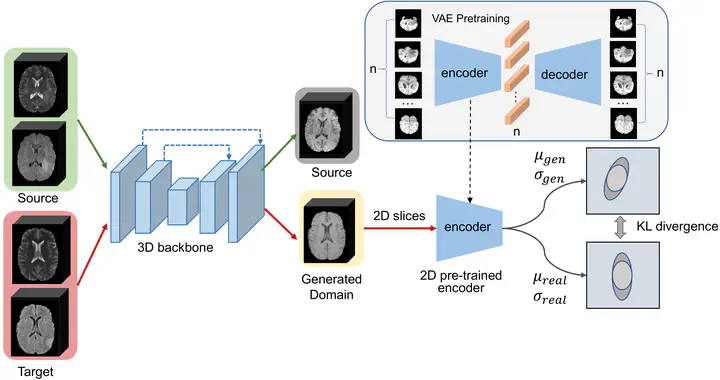
 The main framework of our proposed 3D-UDA method for cross-modality MR image synthesis.
The main framework of our proposed 3D-UDA method for cross-modality MR image synthesis.Abstract
Medical image synthesis has attracted increasing attention because it could generate missing image data, improve diagnosis, and benefits many downstream tasks. However, so far the developed synthesis model is not adaptive to unseen data distribution that presents domain shift, limiting its applicability in clinical routine. This work focuses on exploring domain adaptation (DA) of 3D image-to-image synthesis models. First, we highlight the technical difference in DA between classification, segmentation, and synthesis models. Second, we present a novel efficient adaptation approach based on a 2D variational autoencoder which approximates 3D distributions. Third, we present empirical studies on the effect of the amount of adaptation data and the key hyper-parameters. Our results show that the proposed approach can significantly improve the synthesis accuracy on unseen domains in a 3D setting.